Case Study :
Ram's’s bike, which was parked on the road, was hit
accidentally by a tanker. It got damaged and Ram found that repairing it
would cost a lot of money. So he thought of claiming insurance to lessen his
financial burden in repairing the damaged bike. He had bought the vehicle three
years back. He then got so busy with his job that he just forgot where the
insurance policy papers were. Then one weekend, he searched his entire room and
finally discovered the insurance papers, only to find that the insurance policy
has lapsed as he had not paid the premium on last year. A simple negligence,
cost Ram his half month’s pay.
Benefits of Record keeping
An up to date record keeping will enable you to:
1. Track your money— income (where it comes from) and expenses (where it goes)
2. Provide you an easy reference of your wealth—assets (savings, investment, insurance etc) and liabilities (credit card debt, home loan, educational/ vehicle loan).
3. Organize financial activities like budgeting, saving/investment, tax-paying.
4. Provide an evidence of a financial transaction—repayment of loan, depositing money in bank account, purchase of an asset, etc. This is especially important in case any discrepancy arises over it.
5. Simplify the claim process in case of an emergency (insurance) or damaged good (warranty card).
6. Provide evidence for your entitlement to an after-sales service or other benefits.
7. Keep some faithful person informed about your financial transactions
How to Do the Record Keeping :-
An efficient record keeping can be done
by following 2 steps:
1.
Identifying important records: Dig
out all the papers and records that you may have collected over a period
of time. Begin sorting. Not all records that you have are necessary to retain
over a longer term. Identify the records that are critical from the point of
view of them saving you time and money in future, if need be. (Refer to a
suggested list of records mentioned on the next page).
2.
Develop a method to organize them: The
records should be organised in such a way that they become available
just when you need them. You may want to use paper filing system, safe boxes or
briefcase to store your physical records. Records of your expenses, savings,
investments and a handy summary of where all the other records are, can be
maintained on a paper or in electronic format on a computer.
Make
sure that you keep updating the records, adding new relevant ones and disposing
ones which have lost their value like the 1-year warranties.
Also
keeping a simple calendar of payments due (like credit card bills, insurance
premiums, savings deposit, loan repayment, etc.) will prove a very worthy
financial habit.
Financial Records which require Record Keeping :-
Financial
records and important financial papers that need to be kept safe is given
below. It can be used as a starting point to create a personalized record
keeping list for yourself/your household. Use basic filing system—paper or
electronic—to maintain and access these records easily.
1. An Account Book - A month wise
record of day-to day expenses and income. This is important for planning future
spending and for financial analysis. (For maintaining your accounts, refer the
worksheets in this section.)
2. Income/Employment Records - Salary slips,
payment slips, experience certificate.
3 Income Tax Records -
Tax Deducted at source certificate, acknowledgement of filed returns/ tax paid,
tax exemption documents.
4. Insurance Policies and Receipts of Premiums Paid.
5. Bank Records -
Bank statements/updated passbooks, Deposit slips, Cheque books. Also ATM/debit
cards and their PIN.
6. Debt Records - Credit terms, repayment proof.
7. Credit Card Records -
The card itself, bills paid on credit card will prove helpful to check any
discrepancy in the credit card statement.
8. Purchase Records - Bills (especially of high value
items) warranty cards, service commitments.
9. Record of Investments and Assets Purchased.
10.
Your Financial Goals, Budgets and Plans.
Format for Recording your assets and
liabilities
Assets
|
Amount
|
Liabilities
|
Amount
|
Total Savings in all
|
Borrowings
|
||
the Savings Accounts
|
|||
Home Loan
|
|||
Investment
|
Educational
Loan
|
||
Real estate/Land
|
Personal
Loan
|
||
Gold
|
Vehicle Loan
|
||
FDs/NSC/ RD etc.
|
Business
Loan
|
||
Mutual Fund
|
Credit
card debt
|
||
Bonds/ Debt
|
Other
bills on credit
|
||
Shares
|
|||
Others
|
|||
Insurance
|
|||
Life
|
|||
Health
|
|||
Retirement Plan
|
|||
Pension fund
|
|||
PF/PPF
|
|||
Others
|
|||
Others
|
Others
|
||
Total of Assets
|
Amount A
|
Total of Liabilities
|
Amount L
|
Format to Record Your Income

Format of Expense Summary
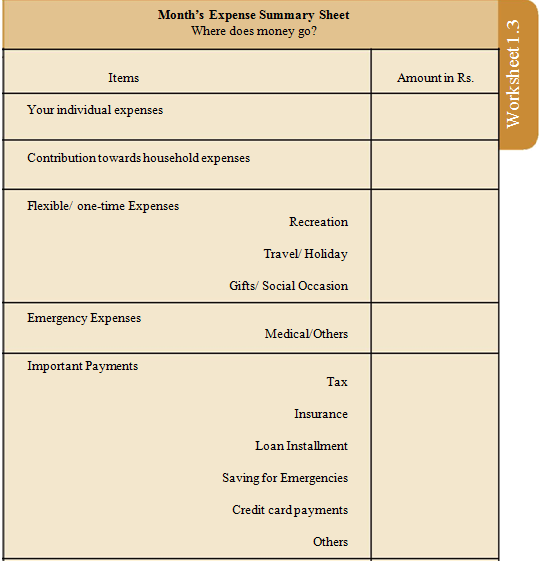
Understanding
your financial position from the records
Check your Financial Position


No comments:
Post a Comment